Cationic resins
🔍 Find UV/LED/EB curing & advanced materials
Cationic resin solutions for UV/LED and EB curing systems
Arkema, through its UviCure® brand, offers a portfolio of cationic resins designed for high-performance UV, LED and EB curing systems.
These specialty materials are based on positively charged (cationic) backbones, enabling dense network formation and durable polymer architectures. Within this technology, cycloaliphatic epoxy resins are key building blocks valued for their high adhesion, low shrinkage, and chemical resistance in epoxy coatings and other performance applications.
To expand formulation latitude, Arkema also supplies oxetane-based reactive components that are typically used in conjunction with cycloaliphatic epoxy resins to enhance speed of cure, adjust viscosity, improve hardness, and promote adhesion to difficult substrates, offering formulators an efficient path to advanced material performance.
Cycloaliphatic epoxy resins
Sartomer’s UviCure® portfolio includes cycloaliphatic epoxy resins designed for UV, LED and EB cationic curing. These high-purity reactive components enable dense and durable crosslinked networks for advanced performance materials.
Key Benefits
- Low shrinkage and high dimensional stability
- High adhesion on a broad range of substrates
- Excellent chemical and environmental resistance
- Durable surface properties with smooth finish
- Fast and efficient UV/LED/EB curing behavior
Main Applications
- High-performance coatings and specialty finishes
- Structural and functional adhesives
- 3D printing photopolymer systems
- Electronics and protective materials
Our brand: UVICURE®

Oxetane diluent resins
Sartomer’s oxetane diluent resins are reactive components used to adjust viscosity and enhance cure kinetics in UV/LED cationic epoxy systems. They improve formulation processability while contributing to performance targets that are difficult to reach with cycloaliphatic epoxy resins alone.
Key Benefits
- Improved adhesion, flexibility, toughness
- Increased thermal stability
- Increased reactivity in UV/LED cationic curing
- Balanced viscosity reduction without loss of crosslink integrity
Main Applications
- High-performance coatings
- Adhesives and specialty bonding systems
- 3D printing photopolymers
- Electronics, encapsulation and protective materials
Our brand: UVICURE®
More information about cationic resins
-
Product catalog - SPEEDCURE Photoinitiators & UVICURE Cationic Resins
-
Product selection guide - SPEEDCURE Photoinitiators & UVICURE Cationic Resins
Technology basics
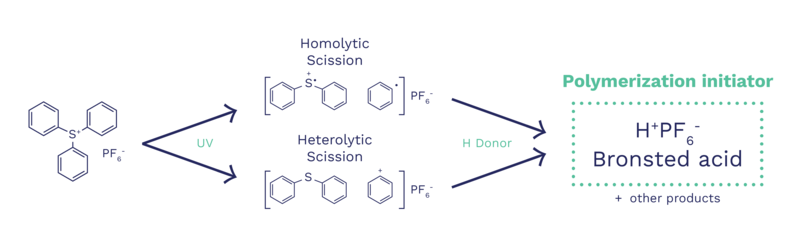
Cationic curing is a photoinitiated, acid catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epoxy resins using onium salts.
Upon exposure to UV light energy and in the presence of a hydrogen donor (typically the resin components of a formulation) cationic photoinitiators produce a long lived acidic species. This species ring opens an epoxy group to form a carbocation which goes on to react with other epoxy groups producing a crosslinked network.
The principle is similar to free radical polymerization: with initiation, propagation and chain transfer steps.
However, only the initiation phase is dependent on the use of a UV light source. All other stages of the polymerization reaction are thermally driven. The acid generated remains active after the removal of UV light energy until it is consumed and the entire film is cured. This is known as dark cure.
Formulations typically consist of 3 materials:
- Photoinitiator onium salts, available under the SpeedCure name.
- Cycloaliphatic epoxy resins, available under the UviCure name.
- Oxetane resins, available under the UviCure name.
Polymerization steps:
1. Initiation – Photoinduced reaction
Upon exposure to UV light energy, onium salt photoinitiators produce a strong Brønsted acid which goes on to propagate the polymerization reaction.
2. Propagation - Thermally driven reaction
The strong acid ring opens an epoxy and/or oxetane

Benefits of cationic curing:
-
Very low shrinkage
-
No oxygen inhibition
-
Excellent adhesion
-
Improved coating properties
-
Dark cure reaction gives high conversion
Learn more about Sartomer® cationic offering
Cationic photoinitiators
Cationic photoinitiators are materials that release positive ions when exposed to light. These photoinitiators can be used in UV-curing applications, where they initiate a polymerization reaction when exposed to UV light. This reaction causes the material to harden and solidify, making it useful for applications such as coatings, adhesives, and 3D printing.
| Name | CAS number | Properties |
|---|---|---|
SpeedCure 937 |
71786-70-4 & 68609-97-2 |
|
SpeedCure 938 |
61358-25-6 |
|
|
SpeedCure 939 |
178233-72-2 |
|
| Name | CAS number | Properties |
|---|---|---|
SpeedCure 976 |
89452-37-9 & 108-32-7 |
|
SpeedCure 992 |
74227-35-3 & 108-32-7 |
|
Often asked questions to our cationic resins experts
Cationic resins are primarily used in high-performance coatings, adhesives, 3D printing (additive manufacturing), and electronics materials where low shrinkage, strong adhesion, chemical resistance and high durability are required. They are well-suited for UV/LED and EB curing systems in industrial, specialty and functional end-uses.
Cycloaliphatic epoxies deliver high adhesion, low shrinkage, and chemical resistance, while oxetane diluents or property modifiers enhance reactivity, flexibility, toughness and substrate bonding. The combination provides formulators with additional latitude to fine-tune film and material performance in advanced cationic and hybrid systems.
